View: Time: 2017-12-15 17:40:30
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) film and polyvinyl butyral (PVB) film is available for two different types of polymer glass laminated structure. PVB has been a reference material for glass bonding in the construction and transportation industry for many years. Due to some favorable performance, EVA is challenging the current PVB as a laminating material. In fact, this type of application is also a good material that meets all the key performance requirements of today's PVB. Not only that, it can also overcome some of the shortcomings of the PVB, beyond the PVB.
Some of the excellent performance of EVA has been proved in the photovoltaic market. In this market, EVA has proved that this fact has been confirmed by the millions of square meters of photovoltaic applications. EVA is a "King" material for the laminating and construction of photovoltaic components, which can generate energy for a long time under extreme operating conditions. At this point, we should remember that the photovoltaic components are being produced and sold for 20 years. At present, other materials have been proved to be more effective than this type of application.
Both EVA and PVB are thermoplastic polymers with some inherent elasticity and natural adhesion properties. Compared with other materials, rigid thermoplastic material appears to be a "chewy adhesive" product at room temperature. In this sense, they are different from the rigid form of thermoplastic plastics, which is why they are named "soft" polymer materials.
Although both are thermoplastic materials, they are different, mainly because their chemical structure is different, as you can notice in these graphs.
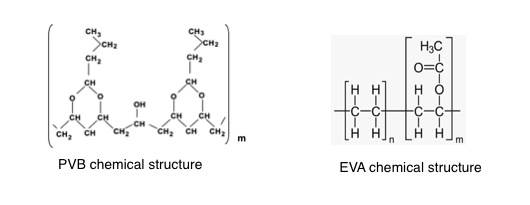
Moleculas_EVA_VS_PVB
From their chemical structure, we can see that PVB basically has only one basic unit that repeats m times on polymer chains (see only one molecular structure in brackets), while EVA has two (see two different group structures). EVA consists of two different repeating units (number: type unit n and type unit m), depending on the number (n times and the other m), depending on how they are allocated to EVA's different performance and performance. According to the molecular composition of EVA, we can see different types. For this reason, EVA can be used in a wider range of applications, because EVA has a better functionality than PVB.
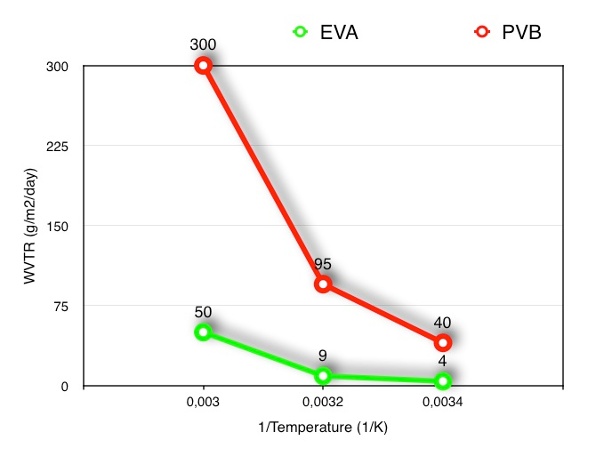
Because of their molecular structure and arrangement, they are amorphous polymers, which is why they all have excellent optical properties and why they are used in laminated glass for building applications.
But it's not just because of their optical properties, why they can be used in architectural applications, but also because of their mechanical properties. Their modulus of elasticity gives them the required properties for diluting the glass - glass size and thermal expansion tension when operating under different weathering environments.
For architectural structures, safety is a vital parameter, regardless of the type of glass laminate. This is why, for example, the building of a fence is not allowed to use a piece of glass to build them. Legislation has forced the use of sandwich glass system to ensure that if one of the glass breaks down for any reason, another glass system will be able to maintain small glass sheets attached to its surface. Security first, the legislative protection of the user, the use of interlayer glasses. The laminating process is seeking to implement the safety elements between the glasses. The main purpose of non glass elements is to provide flexibility for the structure, and the good adhesiveness of glass in the case of broken glass.
PVB or EVA are good materials for this purpose. The difference between them lies in their machinability or ultimate mechanical properties (expansion coefficient, Young's modulus and elastic modulus) depending on their final application and application. The chemical and physical properties of the two materials are very important. The differences in chemical composition and structure between EVA and PVB mentioned above enable us chemists, polymer scientists and chemical engineers to transform raw materials into specific products with different properties and expected properties. Although we can manipulate these materials and drive them along the performance we expect some extension, but for this type of application security is very important, we may consider the use of any kind of "viscous material" they were forced to reach some of the most low value property to meet the required safety standards.
In spite of this, it is important to mention that not all EVA or PVB materials are the same. Under the acronym of EVA and PVB, many different performance products may be considered. It is very important to distinguish all of these by looking at the PDS (product data sheet) that the manufacturer needs to provide. This is the important information that the glass lamination company knows, in order to produce the highest quality laminated glass products according to its laminating equipment and process. But this is not all. Here it is important to point out that the related characteristics of laminated products are final. We mean the qualified certification bodies that any laminates should be satisfied after these materials are laminated and standardized.
Another important feature that the product needs to be met is the adhesion to the glass. As mentioned before, two kinds of polymer materials have acceptable intrinsic adhesion properties, but they can always be increased by using special additives for the corresponding polymer materials. In principle, EVA is a better adhesive material than PVB. PVB has low viscosity for glass. It also has a high degree of advantage.

In addition, in addition to EVA and PVB, other materials can also be used in laminating glass. But most of them are liquid products, and they need to be mixed at least two.

Any problems and get more info, Please Contact us feel free. Email: op@jingglass.com
. Structural Glass Curtain Walls
. What is color! Simple Talking ...
. Advantages and uses of toughen...
. Various glass defects and solu...
Office Addr:Room 1107, B1 Block, Tianan Cyber,Nancheng Area, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China,
Factory Addr:Taiying Industrial, Hongmei Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China
86-769-22273585
86-18145870793
![]()